Network Packet Broker (NPB)
What is a Network Packet Broker (NPB)?
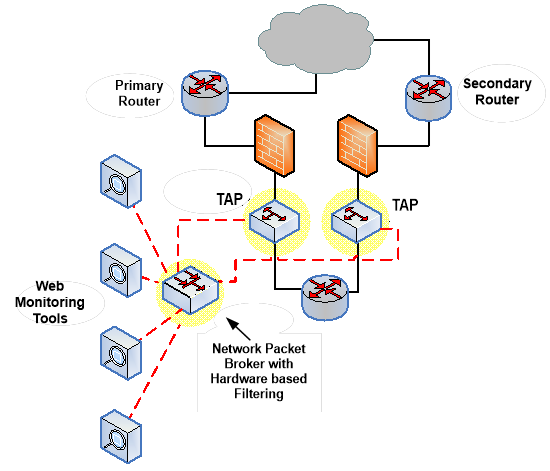
A Network Packet Broker is a purpose-built monitoring infrastructure technology that is installed between an organization's network infrastructure and its security and management tools. Packet Brokers allow organizations to deploy a variety of network tools to access, monitor and analyze network traffic across the enterprise.
Instead of using a dedicated tool to monitor each network segment, network packet brokers can be installed to collect traffic from multiple network connections. They can replicate, aggregate, filter and distribute network packets to assigned monitoring tools. In this way, organizations can not only collect and consolidate all critical data, but also improve the effectiveness and performance of network monitoring and security tools by providing segmented data from across the network.
What are the benefits of a network packet broker (NPB)?
Here are some outstanding benefits:
- Eliminates previously invisible areas in traditional architectures, improves security and enables analysis of all data from critical network segments
- Accelerates the deployment of management, monitoring and security tools by allowing tools to be replaced or upgraded without disrupting the production network
- Future-proofs the IT environment by creating a security and management abstraction layer that separates infrastructure from applications and enables rapid changes and upgrades
- Optimizes technology infrastructure and data center modernization by enabling organizations to better manage all their traffic
- Data deduplication, filtering and slicing reduce overall traffic volume and improve tool efficiency, which lowers operational costs and extends the life of existing infrastructure and connected tools
Click here for an overview of Datacom Network Packet Brokers.
